
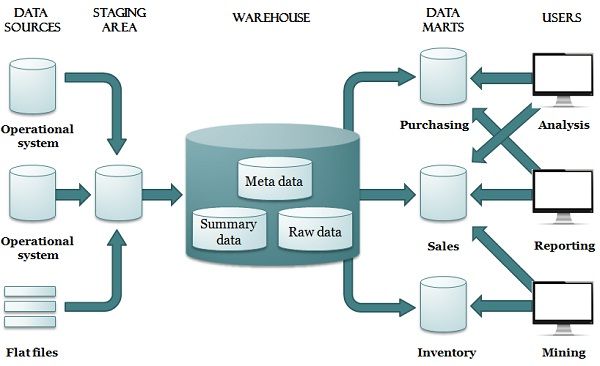
The data in this layer is often in a structured format and is optimized for loading into the data warehouse layer. The data staging layer performs data cleansing, data enrichment, data transformation, and data aggregation to create a consolidated and consistent view of the data. The Data Staging Layer: This layer is responsible for transforming and integrating the data from the source layer into a format that is optimized for loading into the data warehouse layer.The source layer performs basic validation and cleansing of the data and prepares it for loading into the next layer. The data in this layer is in its raw form and is often inconsistent, redundant, and incomplete. The Source Layer: This layer is responsible for collecting data from various sources such as transactional systems, legacy systems, external sources, and other data repositories.The Data Tier is a key component of a data warehousing architecture and typically consists of three main layers, as follows: The data is stored in a structured format, usually a relational database It consists of the actual data warehouse database or databases, along with any associated data marts or data cubes. This tier is responsible for storing and managing the data.
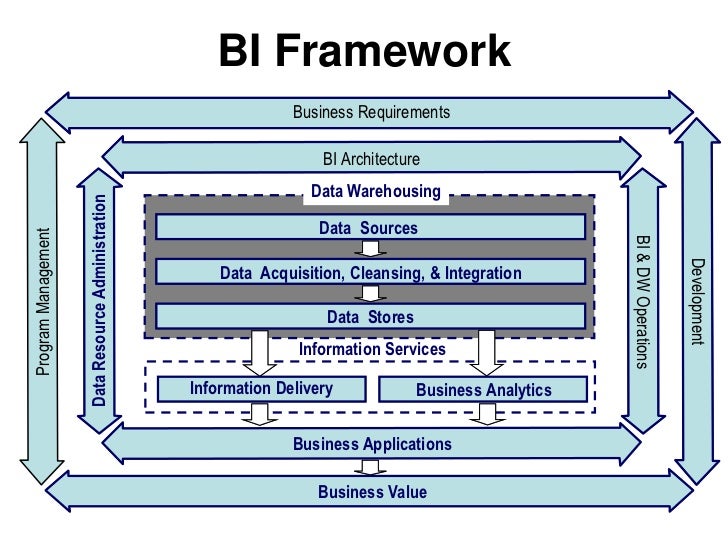
The two-tier data warehouse architecture comprises the following two tiers: This two-tier architecture eliminates the disadvantage of the single-tier because it has a separation between the layers, which is essential in maintaining the two-tier architecture. With the major disadvantage of single-tier architecture not having a separation of layers for analytical and transactional processing, the two-tier architecture of the data warehouse came into play. The goal of having only one physical source layer in a data warehouse architecture is to reduce the amount of data stored to achieve the goal, which eliminates data redundancies. It is also known as an intermediate processing layer, but it is not used on a regular basis in practice. The data warehouse is virtual in this method of single-tier data warehouse architecture, which means that it is implemented as a multidimensional view of operational data, which is mostly created by specific middleware. The physical source layer, the virtual data warehouse, and the analysis layer, which may include reporting or OLAP tools, are all components. In this architecture, all the components required for data warehousing are installed on a single machine, and data is loaded from the operational systems directly into the data warehouse.
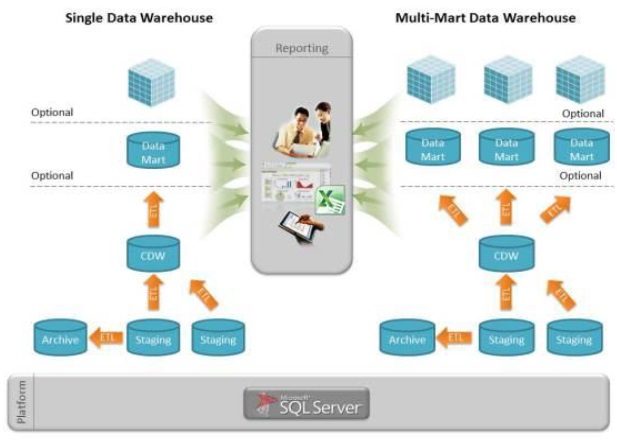
Single-tier data warehouse architecture, also known as basic data warehouse architecture, is a simple and straightforward approach to building a data warehouse. There are three types of data warehouse architecture 1) Single-Tier Data Warehouse Architecture The data warehouse architecture has been the pillar of corporate data ecosystems, and despite numerous changes in Big Data, cloud computing, predictive analysis, and information technologies over the last five years, data warehouses have only grown in importance. Each data warehouse is unique, but they all share certain essential components. In simple words, we can say it is a collection of different data and a data warehouse architecture is a method of defining the overall architecture of data communication, processing, and presentation for end-client computing within the enterprise. What is Data Warehouse Architecture?ĭata warehouse architecture is the design and structure of a data warehouse, which is a centralized repository of data that is used for reporting and analysis. This data is then transformed, cleaned, and integrated into a common format that is optimized for analysis. What is a Data Warehouse?Ī data warehouse is a large and centralized repository of integrated data from multiple sources that have been optimized for querying and analysis. Here we are going to discuss and explore the data warehouse architecture, types of data warehouse architecture, and application of data warehouse architecture. Data warehouses consolidate current and historical data and serve as an organization’s single source of truth. A data warehouse (DW) is a type of digital storage system Its goal is to feed business intelligence (BI), reporting, and analytics, as well as support regulatory requirements so that businesses can turn data into insight and make smart, data-driven decisions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
